We have evolved because we could communicate
If we look at the history of human being and the creation of first civilizations, it is obvious that the human evolved because they communicated. The very simple principle of sharing information and processing data by the human is shown in Figure 1. From bottom to top, the pyramid layers include data, information, knowledge, and wisdom. Data at the bottom is the is the raw material which is processed into information. The data by itself is not valuable until volumes of it can show the patterns and trends. This and other sources of information come together to form knowledge. In a simple statement, knowledge is information that someone is aware of that. Wisdom or intelligence is the baby born from knowledge and experience together. Wisdom is not dependent on the timeline While the knowledge changes over time.
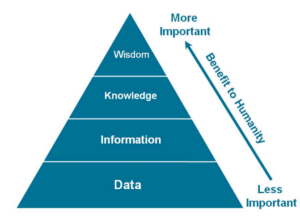
Figure 1. The hierarchy of turning data into wisdom by humans
Source: Retrieved and reproduced from Cisco, (2011)
What is the Internet of the Things (IoT)?
As the technologies evolve and new innovation come on board, people also adapt themselves to a new lifestyle, while the societies continue to modernize and being more connected. Many scientists recognized the last two decades as the fourth global evolution by the Internet. Nowadays, a huge amount of data is collected by a wide range of sensors and then to be transmitted by the Internet to databases and centres through the Internet. By analyzing, and distributing these data on a massive scale, people will have a higher level of knowledge and wisdom which help them to have a more comfortable and sustainable life. This called the Internet of Things (IoT) or the Internet of Objects. It has recently been changing our world, and it is not an incredible statement as we see the impact of the Internet on different aspects of our societies such as in communication, education, transportation, and business. IoT integrates the data, process, objects, and people, in a way to form connected networks in order to give added value to the collected data by turning information into actions that create new capabilities and economic opportunity for businesses.
There has been a lot of discussion on how IoT will affect nearly every global industry—from retail to connected vehicles. IoT has already applied in the sectors such as The Traffic Data Marketplace, Internet of food for tracking and security, Real-time waste management, Health products and services, however, we have to increase our understanding of the success factors, and challenges in each area.
For this purpose, recently there have been attempts to use IoT in horizontal approach rather than vertical applications in the industries, allowing crossing multiple industries. A survey shows that traffic management is one of the most interesting areas for the application of IoT in horizontal approach between actors, while this approach among some other sectors like health-related solutions is still very challenging. Currently, there are many of IoT initiatives that have not been used since many enterprises have the traditional attitude against adaptable and comprehensive IoT solutions. Another obstacle in the application of IoT among different companies is that both the business users and consumers are unsure what the application areas and actual benefits from emerging IoT technologies would be.
Internet of the Things results in value creation
Merely the collection of data does not necessarily mean its effective use. The measured data is a value when it is transformed into valuable information. So in completing the value-loop which is sometimes called optimization, the collected data from its generation is communicated to a place/system to be processed. Information is aggregated over time to be analyzed in ways that guide us for decision-making and implementation. The Information Value-Loop stages of an IoT system is captured in the circle of “Collect→Communicate→Aggregate→Analyze→ Act” in Fig.2, through which the value is created.
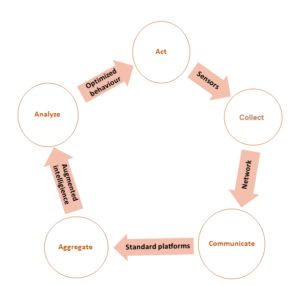
Figure 2. IoT systems’ information value loop
Source: Produced by the Author
For both products and services, companies can use IoT systems to create value through both the value chain. It not only reveals their systems’ performance for each specific product or service but also determines the informational content of their outputs.
IoT: mapping the value beyond our expectations
The Internet of Things, digitalization of our physical surroundings, has attracted significant attention, but to capture the full benefits, we have to understand where the real value is created. In this respect, interoperability between IoT systems/platforms is very important to obtain maximum value. Another point is that the most of the collected data by IoT systems are not analysed and no used currently. Mostly, the collected data are used today for the purpose of fault detection and alarm systems, rather than optimization of operation and prediction of the trends, which both provide the greatest added value. Furthermore, the Business-to-business (B2B) approaches in the scope of the IoT has a greater potential to create value than pure consumer applications.
A dynamic industry is evolving around IoT technology. Like other technology waves, there are opportunities for both incumbents and new players. Digitization blurs the lines between technology companies and other types of companies; makers of industrial machinery, for example, are creating new business models, by using IoT links and data to offer their products as a service.
The impact of the IoT on the Supply Chain
As discussed, connectivity is a big deal for data and systems today. As the more devices can communicate with each other and to human, a higher amount of information could be shared, so faster it is to get stuff done. There are a lot of writings about how IoT will affect all aspects of our lives from retail to connected vehicles.
The global supply chain has much to gain from connectivity and is one of the first and most exciting areas of IoT application among all industries. To revolutionize the supply chain, the IoT has aimed to improve the operational efficiency and create revenue opportunities. Therefore, unsimilar to the thoughts that consider the IoT as a tool to track the goods, IoT is a way to boost the companies’ competitiveness in the market. Among all domains in the supply chain, some areas are more affected by the Internet of the Things, as per below:
The very first benefit of IoT in the global supply chain is considered asset tracking. Both the barcodes and tracking numbers are used as a standard method for managing goods transport. By the introduction of RFID and GPS sensors to track goods, barcodes and tracking numbers are not anymore the most expedient methods. With the new approach offered by the IoT, manufacturers can easily have access to the data such as the temperature of their stores, and the time of the storage for each product, at any point in time. This approach will also help companies to have an effective quality control(QC), no delay in deliveries, and forecasting of product.
Therefore, the end-to-end visibility facilitates the in the supply chain to transform from the push into pull operations. In simple words, through a push model, companies only can guess the approximate number of demands of the products and services in the market. In a pull model, thanks to the IoT, analyzed information about the market demands is provided into the supply chain in order to have real-time adjustments in production, distribution, and delivery of both products and services that results in lower costs and higher efficiency of the entire chain.
In addition, the data collection via the product and goods tracking allows companies to make fine adjustment to their production schedules, storage-schedule, and transport-schedule. as well as improving their relationship with other stakeholders such as shippers through the entire value chain. On-time delivery accompanied by higher quality goods means attracting customers and end users.
Another bonus offered by the application of the IoT in the supply chain industry is inventory and forecasting. The installed sensors on devices and machinery can provide precise inventories, eliminating the humans’ errors. Another impact of the IoT is in creating the Connected Fleets of shipping containers, trucks, last-mile delivery vehicles, and so on to ensure that products to be delivered to the customers, faster.
IoT enables the connect points of purchases and customer sites. It helps to record product sales in real-time. Furthermore, it can be used as a tool to monitor the usage patterns of products for the business end-users. Based on this approach, demand and sales forecasts can be predicted to improve the marketing activities or even to produce the products according to the customer preferences.
From a technical perspective, the Data can be analyzed for signs of impending problems or failure. It is a big favour of the IoT for manufacturers to schedule their maintenances based on preventive-maintenance approach and to minimize the machinery break-down which is costly.
Conclusion
The increasing number of things connected to the internet like machinery with sensors and smartphones along with improved connectivity through the internet and accessibility to the cloud services are altogether expanding the application of the Internet of Things (IoT) in our world.
In the supply chain industry, the Internet of Things technologies allows better management of operations from production through to delivery. Well-connected objects like equipment, vehicles, and inventory produce real-time data. The data is processed to valuable information where analytics are used to spot the trends and new opportunities. Thanks to the predictive approach provided by the IoT for different sections of the supply chain like predictive maintenance in production-lines, synchronised transport in shipment, and market demands’ prediction, the enterprise can resolve the problems before having severed impacts on customers or even on partners. Cloud solutions assist a lot in connecting the different systems in order to help stakeholders of extended supply chains to benefit from the IoT together.
Business models have to choose the IoT technologies to use, based on their priorities. The crucial issues such as security and compliance should also be regarded. If these mentioned aspects are managed properly, supply chains benefit from the Internet of Things for increased visibility and flexibility, faster reaction times to market changes, and new, more competitive supply chain models.
By M. Karimpour, and R. Karimpour

